How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface . environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus.
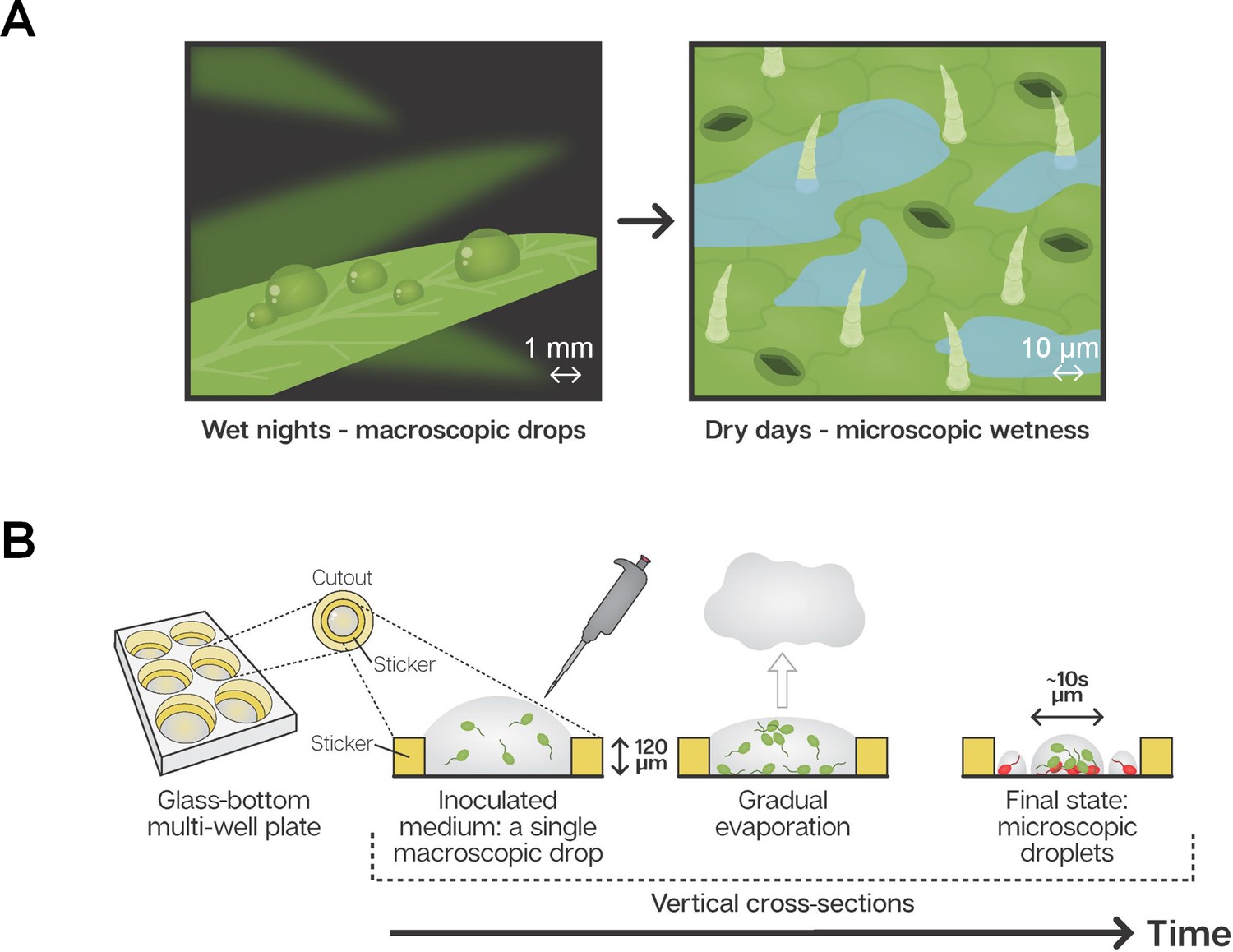
from elifesciences.org
environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable.
Bacterial survival in microscopic surface wetness eLife
How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus.
From www.zidac.co.uk
How Long Can Bacteria And Viruses Live on Surfaces? Zidac How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From www.medicalnewstoday.com
Bacteria Types, characteristics, where they live, hazards, and more How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: Microbes can live on household surfaces for. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From manandmicrobes.com
How do bacteria survive in hydrothermal vents? How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From www.bartleby.com
Answered Bacteria multiply and produce… bartleby How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From www.pinterest.com
How long do microbes like bacteria and viruses live on surfaces in the How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From dxozyufbc.blob.core.windows.net
How Long Does The Staph Bacteria Live On Surfaces at Maria Chisolm blog How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. . How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From hjssupply.com
How Long Can Viruses and Bacteria Survive on Surfaces? How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface the answer is probably not what you want to hear: bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. Microbes can live on. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From hxeyplpjr.blob.core.windows.net
How Long Does Conjunctivitis Bacteria Live On Surfaces at Glenn Jeske blog How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From pngtree.com
Bacterial Microbe On The Surface With Bacterial Bacteria On It How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From sarahs-world.blog
Bacterial growth and how bacteria reproduce on Bacterialworld How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From www.findatopdoc.com
MRSA bacteria can survive on surfaces for weeks FindATopDoc How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. the answer. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From dxocfufdi.blob.core.windows.net
How Long Can Germs Last On Fabric at David McDonald blog How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From sciencenotes.org
Examples of Bacteria in Everyday Life How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. the answer is probably not. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From studybreathings.z21.web.core.windows.net
How Long Does Bacteria Take To Multiply How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface Microbes can live on household surfaces for hundreds of years. while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. some viruses and. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From info.chempacs.com
How Long Can Viruses & Bacteria Live on Surfaces? How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface the answer is probably not what you want to hear: the longer a microorganism may persist on a surface, the longer the contaminated surface may be a source of transmission and thus. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. Microbes can live on. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From aestheticsjournal.com
Infection Control Aesthetics How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface while on cotton, the bacteria have been shown to survive for up to 21 days, living cells could be detected for up. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. bacteria may. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From studybreathings.z21.web.core.windows.net
How Long Does Bacteria Take To Multiply How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface some viruses and bacteria can live on surfaces just for a few hours or a day, while others can survive for a few weeks or even months washing. the answer is probably not what you want to hear: bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.
From exotuevtd.blob.core.windows.net
Strep Bacteria Live On Surfaces at Gloria Mosley blog How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface environmental surfaces may serve as potential reservoirs for nosocomial pathogens and facilitate transmissions via. scientists have found that many potentially infectious bacteria, viruses, yeasts and moulds can survive on surfaces for considerable. bacteria may highly differ in their potential to survive on such surfaces, but up to now there are only few data. while on cotton,. How Long Does Bacteria Live On The Surface.